Why Do Microwaves Heat Food Unevenly? (Best Way to Fix It)
Microwave ovens are a convenient and quick way to cook. They can be used for many different types of dishes, but there is one problem: they don’t always cook evenly!
Do you want to know why microwave ovens don’t cook evenly?
Key takeaways
- Microwaves cook unevenly due to the standing wave pattern they create inside the oven, which results in certain spots receiving more energy than others.
- The shape and size of the food item, as well as its placement in the oven, can affect how evenly it cooks in the microwave.
- Rotating the food item or stirring it during cooking can help distribute the energy more evenly and result in more uniform cooking.
- Microwaves cook food by exciting water molecules, so foods with higher water content will cook more quickly and evenly than those with lower water content.
- Using microwave-safe cookware and following recommended cooking times and power settings can also help ensure more even cooking in the microwave.
Why do microwaves cook unevenly?
Microwaves cook food unevenly due to the behavior of the radiation they emit, which moves in a fixed path and bounces off the walls of the microwave chamber. This means that if certain areas of the food are not in the path of the radiation, they will not be heated, resulting in cold zones.
While microwaves have built-in turntables to help distribute the radiation more evenly, it is not a perfect solution.
Also, the density, thickness, and shape of the food, as well as its position and the power settings used, can all affect how evenly it is cooked.
To minimize uneven cooking, it is recommended to select the appropriate power settings, use microwave-safe containers, and cover the food with a lid or wrap to help trap in heat and promote more even cooking.
Spacing out the food on the turntable and turning it over occasionally can also help to promote more even cooking.
Reasons why microwaves cook unevenly
- Food density: Different parts of a food item may have different densities, which can affect how quickly they heat up in a microwave. Dense areas may absorb more heat and take longer to heat up, while less dense areas may heat up more quickly. For example, a baked potato may heat up more slowly in the center where it is more dense, while the outer edges may become too hot and dry out.
- Position in microwave: Food items placed in certain areas of the microwave may be exposed to more or less radiation than others, which can lead to uneven heating. The areas closest to the walls of the microwave may receive more radiation than the center, causing uneven heating. It is important to stir or rotate the food during cooking to ensure even heating.
- Thickness of food pieces: Thicker pieces of food may take longer to heat up than thinner ones, resulting in uneven heating. This is because the microwaves penetrate only a certain depth into the food before being absorbed. As a result, the outer portions of the food may be overcooked or dry before the center is fully heated.
- Type of food: Different types of food may have different water or fat content, which can affect how they heat up in a microwave. Foods with a high water content, such as vegetables, tend to heat up more quickly than foods with a low water content, such as bread or meats. Foods with a high fat content, such as bacon or cheese, tend to heat up more slowly than other foods because fat absorbs less microwave radiation.
- Microwave power settings: Different power settings can result in different levels of heat being applied to food items, which can lead to uneven heating. Using a high power setting can cause the outer portions of the food to overcook while the center is still undercooked. Using a low power setting can cause the food to cook more slowly and unevenly.
- Shape of food pieces: Food items with irregular shapes may heat up unevenly compared to more uniform ones. For example, a whole chicken may heat up unevenly due to its irregular shape, with some portions becoming overcooked while others remain undercooked.
- Turntable functionality: If the turntable in a microwave isn’t working properly, certain areas of the food may not be exposed to radiation, resulting in uneven heating. It is important to ensure that the turntable is functioning properly and that the food is placed in the center of the turntable for even heating.
- Food containers: Certain types of containers may heat up more quickly than others, which can lead to uneven heating of the food inside. For example, plastic containers may not heat up as quickly as glass or ceramic ones, leading to uneven heating. It is important to use microwave-safe containers that are appropriate for the type of food being cooked.
- Microwave heat absorption: Some foods absorb microwave radiation more readily than others, which can result in uneven heating. For example, foods with a high water content, such as vegetables or fruits, tend to absorb microwave radiation more readily than foods with a low water content, such as meats or bread.
- Microwave radiation density: The intensity of the microwave radiation can vary across the oven, which can result in uneven heating of food items. This can be due to a number of factors, such as the design of the microwave, the power output, or the age of the appliance. It is important to stir or rotate the food during cooking to ensure even heating.
Tips on how to evenly cook food with a microwave
Here are a few tips I think will help you prevent and avoid your food from having too many cold spots. Microwaves, no matter how advanced they are, will have cold spots. It’s just the nature of the design and the physics that bind it from being a full-body cooking machine.
1. Make sure you stir your food
In between microwave cooking, simply stop the microwave and stir the food completely. This will help distribute and spread out any hot spots from each other to make sure that your meal is fully cooked, not just part of it.
This works well for mixtures of food like soups, creamy and chunky meals.
2. Spread your food out
This probably goes without saying, but as I explained above, microwaves can only travel so far into the food.
The thicker the item being microwaved, like a steak for example…the larger its interior will be and this can lead to cooking inconsistencies or cold spots.
The best way in my opinion is just simply to make sure you spread out your meal as evenly as possible on whatever plate that’s going into it.
This means meat should be separated from the sides on a plate that’s large enough, or if you’re microwaving a single item like bread, it should be laid out on the plate in an even layer.
3. Move your plate to the outer edge of the spinning plate
You can even punch a hole into the middle section of the plate devoid of food. This is similar to what a donut would look like. What this does is it gives the food a better chance at being cooked more evenly.
If you think about this, it makes sense.
Picture how much movement you get if you were to place yourself at the end of a spinning circle. Then picture how much movement you’d get if you were placed in the middle of this spinning circle. You’re not going anywhere in the middle.
Leaving food mostly on the furthest end of a spinning place can help make it more probable that it will make contact with heated spots.
4. Place a lid over the container
In this method, I’m not saying you should place a lid over the bowl and shut it tight. That might either damage the lid or cause a pressure build-up.
What I mean is just to place the lid over the top of the bowl. Allow small areas where air can escape to avoid the buildup of pressure and any problems with contacting food or condensation.
This method attempts to prevent heat and hot moisture from leaving the vicinity of the bowl too quickly. With heat and moisture trapped between the food and the lid, it has a better chance of conducting itself back into the food keeping it one step warmer.
5. Let it sit after cooking
Heat dissipates. This means that if you leave heat alone, it will try to spread out naturally. My advice would be to allow the heat time to spread as far as it can throughout the microwaved meal.
I’m sure you’ve noticed how a lot of frozen dinners will have instructions on the back of the box with the last direction to let it sit for x amount of minutes.
This serves two purposes. One is to not burn the meal prepper, and the second is to allow the heat to evenly spread throughout the food.
6. Buy using a food thermometer
You can dig it into the center of your steak or mixed set of food to check the temperature. Refrigerators normally keep foods cold at 40° F (4° C). So anything close to this number is potentially not cooked.
7. Cook at lower power
One thing I’ve recently discovered is that cooking at lower power on a microwave really doesn’t mean that it has the ability to actually lower its temperature or heating power.
It isn’t a dial like what you would find in a stovetop oven. Lowing the power settings simply forces the microwave cycle between turning on and off throughout the cooking time.
If you listen very closely, you might even hear the magnetron turn itself on and off through a humming noise.
During the offs, the heat can potentially dissipate throughout the food and cook more evenly.
8. Select the right setting for the job
Different types of food require different power settings and cooking times.
Refer to the manufacturer’s instructions or a microwave cooking guide to determine the appropriate setting for the food being cooked. Using the wrong setting can result in uneven cooking.
9. Make sure the turntable is in the right position
The turntable in a microwave helps to ensure even cooking by rotating the food as it cooks.
Make sure the turntable is in the correct position before starting the microwave. If the turntable is not rotating, it may need to be cleaned or repaired.
10. Use a lid to cover the container
Using a lid to cover the food during cooking can help to trap steam and distribute heat more evenly.
This is especially important for foods with a high water content, such as vegetables or soups. It is important to use a microwave-safe lid that fits the container being used.
11. Try different food densities
As mentioned earlier, food density can affect how quickly food heats up in the microwave.
If uneven cooking is a problem, it may be helpful to try cutting the food into smaller or thinner pieces to promote more even cooking.
12. Debone the meat
Meat with bones can heat up unevenly in the microwave, resulting in undercooked or overcooked portions.
If possible, it is best to remove bones before cooking to promote more even cooking.
13. Use smaller microwave-safe containers
Using smaller containers can help to promote more even heating by allowing the food to heat up more quickly and evenly.
Use microwave-safe containers that are appropriate for the type of food being cooked.
Top 3 meat thermometers you should consider

- Instant and highly accurate thermometer
- Multi-use for various types of food
- Easy-to-read digital display
- Water-resistant and washable
- Ideal gift for cooking enthusiasts

- Extended 500ft remote range, dual probe
- Hassle-free setup and use
- Convenient kitchen timer feature
- Preset USDA temperature settings
- Accurate, durable probes with high temperature resistance
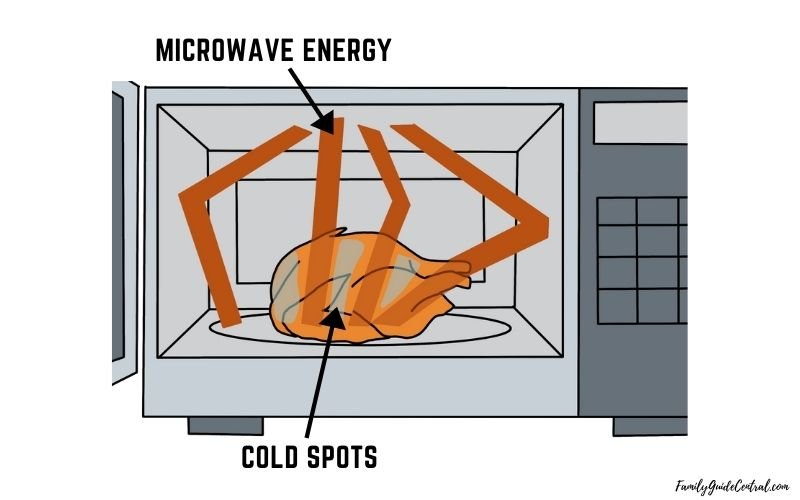
Microwave rays contain areas that don’t produce heat
The real answer lies in the physical of the radiation rays and how they behave. When you continuously emit rays of waves into a chamber like a microwave that doesn’t spin your food, you’ll find cold spots.
This is because the waves in a microwave don’t spread evenly throughout the food. The rays will bounce a few times around the walls and some of them will make contact with your food and some won’t.
Take a look at the picture above. The wave parts that are moving up and down are where the heat is produced. However, its the red dots or what most people call the nodes that stay still and don’t produce head causing the cold spots
These waves can also be described as standing waves that go up and down with certain points that just stay still called nodes. These nodes are where no energy is emitted while the waves moving up and down is where heat is produced.
If you find a cold spot on your meal, that’s probably the area where the node resided.
Almost all microwaves try to solve this issue by making the bottom plate spin so that the food will have a better chance of making contact with the ray. This works. Unfortunately, it’s not perfect. You’ll still find cold spots.
Some microwaves have settled on moving the waves inside the compartments of the microwave instead. And this has helped as well. These are microwaves use a fan above the chamber that helps reflect the microwave beams to different locations as it turns.
Waves have trouble penetrating food that is too thick
When you are trying to cook a very bulky, very thick type of food such as a thick steak, you’ll notice more cold spots.
The reason being is again due to how the microwave rays heat. When two opposing microwaves collide, it is at that point where heat is produced. Now, the waves can only travel so far into that piece of meat. And the cold spots are created because there is less heat being produced at those points in time
The thicker it gets, if you do not adjust cooking times accordingly also with microwaves that don’t have a rotating tray inside then more of these hot and cool zones will start to emerge as well.
Microwaves don’t cook frozen foods well
Frozen food is an interesting case study. Ice is extremely dense and microwaves can’t often cook icy foods well. The problem with placing a frozen meal into a microwave is that for one thing, it can’t penetrate ice as well as water.
When that ice transforms into water.
Now in the water state, microwaves have no problem cooking water up really fast. This results in what you can imagine as a slow, then fast cooking process. Obviously at this point, if other areas of the food are still frozen, there’s a good chance the water areas are already cooked.
This creates an imbalance of effective heating, thus, adding to the hot and cold spots dilemma.
Does the microwave cook food less evenly than a regular oven?
The microwave and the regular oven have different methods of heating, and as such, they have different strengths and weaknesses when it comes to cooking food.
While the regular oven uses radiant heat to cook food from the outside in, the microwave uses electromagnetic waves to heat the water molecules in the food directly. This means that the microwave can cook food faster than the regular oven.
However, the microwave can sometimes result in uneven cooking, with some parts of the food being cooked more than others.
This is because the microwaves penetrate the food unevenly, depending on factors such as the shape of the food and the position in the microwave.
In contrast, the regular oven can produce more even cooking because the heat is distributed more evenly throughout the oven.
Why is microwave food cold in the middle?
Microwave food can sometimes be cold in the middle because the microwaves are absorbed by the outer layers of the food, while the inner layers are slower to heat up.
This can be particularly problematic for denser or thicker foods, as the microwaves struggle to penetrate the food all the way to the center.
Also, microwaves tend to cook food from the outside in, meaning that the outer layers can become overcooked while the middle remains cold.
To avoid this problem, space out the food and turn it over occasionally to ensure that it cooks evenly.
Why do microwaves cook food so much faster than ovens do?
Microwaves cook food faster than ovens because they use electromagnetic waves to heat the water molecules in the food directly.
This means that the food is heated from the inside out, rather than from the outside in like in an oven.
Also, the microwave’s energy is concentrated directly on the food being cooked, while the oven’s heat is spread out over the entire oven, including the air inside.
This makes the microwave more efficient at heating up food, resulting in faster cooking times.
How does power level affect cooking in the microwave?
The power level of a microwave affects how quickly the food is heated, with higher power levels resulting in faster cooking times.
However, higher power levels can also result in uneven cooking, as the microwaves can penetrate the food too quickly and cause the outer layers to overcook while the inner layers remain cold.
Lower power levels can help to promote more even cooking by allowing the food to heat up more slowly and evenly.
I recommend checking with the manufacturer’s instructions or a microwave cooking guide to determine the appropriate power level for the food being cooked.
What’s the difference between the different wattage use of microwaves?
The wattage of a microwave refers to how much power the microwave uses to generate microwaves.
Microwaves can range in wattage from around 600 watts to over 1200 watts. Higher wattage microwaves can cook food more quickly than lower wattage microwaves, as they generate more energy.
However, higher wattage microwaves can also result in uneven cooking, as the microwaves can penetrate the food too quickly and cause the outer layers to overcook while the inner layers remain cold.
Lower wattage microwaves can help to promote more even cooking by allowing the food to heat up more slowly and evenly.
Where is the hottest place in a microwave?
The hottest place in a microwave is generally in the center of the microwave, where the microwaves are most concentrated.
This is why most microwaves are equipped with a turntable, which rotates the food as it cooks to ensure that all parts of the food are exposed to the microwaves.
Also, the walls of the microwave can also become hot during cooking, so it’s recommended to use microwave-safe containers that can withstand high temperatures.
Avoid overcrowding the microwave, as this can prevent the microwaves from reaching all parts of the food and can result in uneven cooking.
To ensure that the food is cooked evenly, it is important to properly space out the items on the turntable and to turn them occasionally. Also, using a lid or covering the food can help trap the heat and promote more even cooking.
You can test this yourself
If you are interested in seeing this with your own eyes, try this. Get a few chocolate candy bars and lay them flat on a tray. Try to cover the tray up as much as possible but also make sure the candy bars are all laying flat side-by-side.
Remove the spinning tray from the microwave and place the tray full of chocolate bars into the microwave. We don’t want the rotating tray to move the tray. We want the tray to stay in one place.
Turn on the microwave and let it cook for about 30 to 40 seconds. When done, remove the tray of chocolate and examine how and where on the tray the chocolate bars have melted.
You’ll notice that only certain spots of the chocolate are melted, not the entire chocolate.
The heated area is cooked but the uncooked area is what we call the cold spots.
You should now start to develop a theory about how microwaves cook and recognize that microwaves do, in fact, cook unevenly.
Don’t eat food that’s not fully cooked
Uncooked food is a breeding ground for bacteria. The main reason that we cook most, if not, all of our food is that we want to kill off any bacteria that might be living or growing on food. Heating our food up will most likely kill the majority of harmful bacteria that might be living on our food.
The main reason for this is that bacteria will not survive at temperatures above 140 degrees Fahrenheit, and microwaves can cook up to a temperature of about 170-180° F (77 – 82 °C).
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), most bacteria are killed when temperatures on food reach or exceed 149°F (65°C).
However, as stated in this article, cold spots do happen, and if those bacteria are found in these cold spots, there’s a good chance they are alive and well.
Other interesting topics:

